GDataXML is Google’s XML processing library. We have choosen GDataXML since it performs well for DOM parsers, supports both reading and writing, and is so easy to integrate. However, if you are using a different DOM parser, it should be almost exactly the same as this but just slightly different API calls.
Design Phase: For this sample application we will parse an XML file that is present in the bundle and display its content in the table view.
Before beginning with this tutorial you have to download the GData library from below link
Step 1: Open Xcode and select the windows based application template and add UITableViewController subclass file to it with the name MyTableViewController, after doing this their would be two files that would be added into your class group [MyTableViewController.h and MyTableViewController.m].
Step 2: Add the GData library into your project so for that select the downloaded GData file from the download folder and inside the folder you will find a folder with the name source and then inside the source folder you will find a folder named “XML support”, drag and drop this folder into your application. Make sure you add this by selecting the copy files into destination folder option.
Once this is done then we will have to do some settings so that GData library works nicely with our application.
Perform the settings that are given below:
1) Select the project tab from the xcode menu and select the edit project settings option
2) You will see a window in front of you that’s your project window from there select the header search path option (you can type header search path in the search bar) and type the following that is given in the image below
3) Once you are done with header search path the other setting that you have to do is set the other linker flag (you may type other linker flag in the search bar), now once you find the other linker flag just type the following data in the image given below
4) Now its time to test whether you have made the correct settings or not and for that you have to import the GDatatXMLNode header file in the .h file of the MyTableViewController class and press build your application.
Step 3: Here’s a look at our XML file, which is present in the bundle, now in order to read this file just follow the steps given below
First in the .h file declare the following objects, I have used comments to describe the objects,
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import "GDataXMLNode.h"
@interface MyTableViewController: UITableViewController {
//stores the entire data about the XML document
GDataXMLDocument *xmlDocument;
//string variable to hold the location of the XML File
NSString *xmlFileLocation;
//after parsing the data will be stored in the array
NSMutableArray *data_from_xml;
//stores the error information that occured
NSError *error;
}
@end
Now into the .m file, select the init method and add this piece of code.
-(id)initWithStyle:(UITableViewStyle)style {
if (self = [super initWithStyle:style]) {
xmlFileLocation = [[NSBundle mainBundle]pathForResource:@"Cars" ofType:@"xml"];
NSData *xmlData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:xmlFileLocation];
xmlDocument = [[GDataXMLDocument alloc]initWithData:xmlData options:0 error:&error];
NSArray *getData = [[xmlDocument rootElement]elementsForName:@"car"];
data_from_xml = [[NSMutableArray alloc]init];
for(GDataXMLElement *e in getData)
{
[data_from_xml addObject:e];
}
}
return self;
}
Step 4: Now once the above step is completed then just add the number of sections and rows for section in the datasource method of the table view, here’s a view of doing that
#pragma mark Table view methods
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return 1;
}
// Customize the number of rows in the table view.
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return [data_from_xml count];
}
Now its time to see some real GData
In the cell for row at index path method when you give title to each cells then in this case the titles will be coming from the XML file so for that what you have to do is select the appropriate elements from the XML file and display them in the table view and here’s how you do that
// Customize the appearance of table view cells.
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
static NSString *CellIdentifier = @"Cell";
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
if (cell == nil) {
cell = [[[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle reuseIdentifier:CellIdentifier] autorelease];
}
// Set up the cell...
cell.textLabel.text = [[[[data_from_xml objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]elementsForName:@"company"]objectAtIndex:0]stringValue];
cell.detailTextLabel.text = [[[[data_from_xml objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]elementsForName:@"model"]objectAtIndex:0]stringValue];
return cell;
}
Step 5: Select the AppDelegate.m file and add the table view to the window. Here is how you will do that.
#import "GDataAppAppDelegate.h"
#import "MyTableViewController.h"
@implementation GDataAppAppDelegate
@synthesize window;
- (void)applicationDidFinishLaunching:(UIApplication *)application {
// Override point for customization after application launch
MyTableViewController * mtvc = [[MyTableViewController alloc]initWithStyle:UITableViewStyleGrouped];
[window addSubview:mtvc.view];
[window makeKeyAndVisible];
}
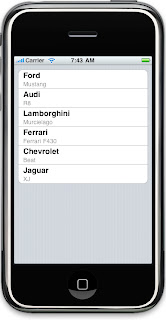
Click build and go you will see the output as given below
Summary
In this post, we have read the xml document using a dom parser. Now using GData you can also write an xml file to store your applications data. We will soon have a tutorial for that as well.